Publication des bureaux d’études Smart Systems
10 février 2022Bonjour à tous,
Aujourd’hui, de nouveau un post sur la publication des articles produits par les élèves de 3ème année les projets Smart Systems de la filière SEM l’Ense3.
Je vous souhaite une bonne lecture,
Jérôme Ferrari
Projet 1: Contrôle de la qualité de l’air
Auteurs
- Corentin Jacquier
- Simon Jouve
Résumé
En cette période de pandémie, on nous a beaucoup incité à ventiler notre air intérieur afin d’éviter la
propagation du virus. En effet, une mauvaise ventilation permet au virus de s’accumuler et donc de
contaminer plus facilement. Même en temps normal, il est important de conserver un air intérieur
d’une bonne qualité pour éviter l’accumulation de composés nocifs comme les bactéries ou les
moisissures. De plus, avoir une pièce bien ventilée permet de vivre dans un meilleur confort car par
exemple une pièce trop humide est désagréable.
Ainsi, pour conserver un air agréable et sain, un bon contrôle de la ventilation est nécessaire. C’est
dans cette optique là que s’inscrit notre projet.
Rapport
Code
Projet 2: Etude pour un dimensionnement optimal de la puissance du compteur électrique
Auteur
- GAUTHIER Esteban
- TREREMI Romain
Résumé
De nos jours, la technologie “Internet of Things” (IoT) connaît un essor considérable.
L’IoT désigne la connexion des objets et des systèmes techniques à Internet, notamment
à travers l’agrégation de données et la multiplication des capteurs. Les notions de cloud
et d’objets connectés ouvrent le champ des possibles concernant le pilotage intelligent
des systèmes et l’optimisation des flux de consommation d’énergie.
Notre analyse portera plus particulièrement sur l’étude du profil de consommation de la
maison afin d’optimiser le contrat de souscription de puissance électrique. La puissance
du compteur électrique, exprimée en kVA, correspond à la puissance maximale que peut
délivrer le compteur électrique. Ce seuil doit théoriquement supporter la puissance
atteinte lorsque tous les appareils électriques de la maison fonctionnent en même
temps. Si la puissance soutirée dépasse le seuil du contrat électrique, le compteur
disjoncte d’où la nécessité de calibrer son abonnement de sorte à ne pas être sujet à des
coupures régulières.
Article
Code
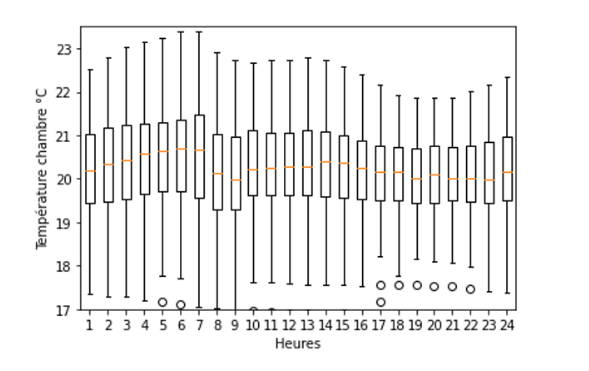
Projet 3: Étude des variations des températures intérieures et estimation de la surconsommation liée au surchauffage de l’habitat
Auteurs
- Matthieu Ernst
- Baptiste Journaux
Résumé
Face aux enjeux du réchauffement climatique, l’action de chacun est nécessaire pour réduire les
émissions globales des gaz à effet de serre. La programmation pluriannuelle de l’énergie (PPE), or-
ganisme d’Etat, fixe des objectifs de réduction des consommations d’énergie des ménages à -16,5% à
l’horizon 2028 1. Puisque le chauffage représente plus des deux tiers de la consommation énergétique
totale d’un ménage, nous avons choisi de travailler sur une étude des variations des températures
intérieures et estimation de la surconsommation liée au surchauffage d’un habitat.
Rapport
Code
Projet 4: Influence of outside temperature on
consumption habits
Auteur
- ACKERMANN Antoine
- DA NASCIMENTO Manon
Résumé
This study proposes an analysis on the impact of outside temperature on electricity
and gas consumption. The aim of this study is to observe if temperature modifies the
consumption habits of a household. Five measures were read from September 2020 to
January 2022 : total daily electricity consumption, daily TV consumption, daily hotplates
consumption, daily washing machine consumption and daily gas consumption. No clear
correlations were found between outside temperature and the four former measurements,
which are all electric appliances. On the contrary, there is an evident link between gas
consumption, that is being used for space and water heating and outside temperature.
Article
Code
Projet 5: Occupancy of a Smart Home
Auteur
- Michel Farah
- Paula Alejandra Pedraza Aguirre
Résumé
This paper analyses the correlation between four types of variables (CO2 emissions, total power,
total power of a TV and noise) using the machine learning method known as K-mean clustering to
estimate the occupancy of a room. The analysed data are obtained from the study of a household
through the Expe-smarthouse project, which provides the opportunity to access in real time through
a Grafana portal with Influxdb database. Additionally, the selected sensors and data are studied
individually to better understand their behaviour. The methodology used corresponds to the collection
of data through the installation and correct execution of the different softwares, the subsequent selection
of relevant data and its management by means of appropriate statistical techniques to obtain the same
step time of analysis. Finally, the application of the clustering method that allows the variables to be
related and to conclude about the occupation.
Article
Code
Projet 6: Electricity Consumption Estimation
Auteurs
- André IMANISHI LOPRETTO
- David Samuel EYHORN
Résumé
Due to increasing share of renewable energies in the electricity mix and resulting
volatility of electricity generation demand prediction and demand response becomes
more and more important. Electricity demand often correlates with weather conditions,
e.g. the demand for indoor lighting increases when it is more clouded. At the same time
solar panels are producing less electricity during this time. This requires prediction of
the electricity demand to ensure grid stability and activate backup resources in time.
Grid operators can then coordinate the required generation to meet the demand.
In this study we are analyzing the performance of a decision tree classifier to estimate
the electricity consumption of a residential house near Grenoble based on weather data.
The variables used are humidity, luminosity and temperature. Gas heating is installed in
the house.
The goal of this study is to find the weather variables that are most suitable to be used
for these kinds of predictions and find explanations for our results. However, the goal is
not to achieve the most accurate results possible. To achieve a more accurate
performance many more variables, e.g. previous energy consumption (one week ago,
one day ago,..), must be included.
Article
Code
Projet 7: Analysis of the level of discomfort in a given smart home
Auteurs
- Elsa Magré
- Rebecka Trångteg
Résumé
In a world facing climate change it is important to reduce the use of energy to minimize its
environmental impacts. Since the building sector takes up a great share of the energy use it
is important to make energy reducing measurements there. One key player in energy use
reducements is smart sensors. Smart sensors can also be used to create a better indoor
environmental quality which is important to take into consideration. In this project, the level of
discomfort in a given house with given data has been examined. The given data showed that
there are many parameters in the house that reach the thresholds for discomfort.
Article
Code
Projet 8: The Environmental Effects of Smart Homes
Auteurs
- ABDUL SAMAD EL SKAFF Yara
- LANDOLSI Mohamed Aymen
Résumé
Nowadays, more than ever before, people are becoming more and more aware about the effects
their daily lifestyle is having on the environment. The subject of climate change and other threatening
environmental issues is one of the most shared topics today.
Smart Homes are a new concept that has seen a lot of attention during the last few years. A smart
home is a home where most appliances (TV, lighting, heating. . . ) are connected through the internet.
This allows users to monitor their appliances and control them whenever needed through their mobile
phones.
Although this concept may seem to not have that much effect on the environment, the reality
is contrary. A study conducted showed that smart homes can reduce energy consumption and CO2
emissions by 13% [1]. Not to mention the opportunity it offers for consumers to track their lives and
completely control their home which largely increases their engagement in the environmental aspects
throughout their everyday lives.
In this paper, we will be using data extracted from a real smart home [2], and studying the effect
this smart home has on the environment through the daily behaviors of its occupants.
Article
Code
Projet 9: Étude de différents paramètres pouvant impacter ou être impactés par l’utilisation de la machine à laver au sein d’une habitation
Auteurs
- Florent Vince
- Alban Doublet
Résumé
Un appareil électroménager tel qu’un lave-vaisselle ou un lave-linge représente une
part non négligeable de la consommation d’eau et d’électricité d’un foyer ; aussi, parvenir à
réduire la consommation d’un tel appareil présente un intérêt économique et écologique
évident.
Afin de pouvoir optimiser la consommation liée à un appareil électroménager, une
première étape est de déterminer quels autres paramètres sont éventuellement corrélés à
l’utilisation de cet appareil. Identifier les paramètres influant sur l’usage de l’appareil permet
en effet d’identifier les habitudes de l’utilisateur, afin de chercher dans un second temps à
optimiser l’utilisation de l’appareil. On s’intéresse donc ici à l’impact de certains paramètres
sur l’utilisation d’un lave-linge dans une maison intelligente, ainsi qu’à l’impact de l’utilisation
de ce lave-linge sur d’autres paramètres.
Article
Code
Projet 10: Estimating window opening in a room
Auteurs
- Garat Alexandre
- Saint omer Jeanne
Résumé
Smart systems are now everywhere in our life. Our smartphones, our cars, our
buildings, have a lot of sensors. With the Internet of Things (IoT), huge amounts of
data is sent every second. To be useful these data have to be treated, to determine
some habits or to predict some behaviors.
More and more people want to have automatic and well-adapted autonomous systems
that can ideally predict their desires and also intelligently reduce their consumption
without losing comfort. It is only the beginning of the data analysis field. Informatic
tools are the key for analyzing and building models.
The purpose of this study is to analyze the impact of opening the window in a room on
life and health parameters such as temperature, humidity or amount of CO2. Then,
building a model that will be able to predict when the room is ventilated or not. This
work will be helpful to detect if the window of a room is open, in particular in the case
where this was not desired due to an oversight of the closure of the window or a
problem. This could also replace windows sensors and allow some money savings.
Article
Code
FIN